In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, understanding the intricate processes that underpin its operation is crucial for developers, researchers, and enthusiasts alike. One powerful tool that can shed light on these complex mechanisms is the use of sequence diagrams. These visual representations can effectively delineate the interactions within a blockchain network, encompassing key aspects such as transaction validation, block creation, and consensus mechanisms.
Blockchain technology has captured the imagination of individuals and organizations across various industries, from finance to supply chain management. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature has made it a transformative force in the digital landscape. However, the inner workings of a blockchain network can often appear opaque, hindering the ability of stakeholders to fully comprehend and optimize the system.
The Power of Sequence Diagrams
Sequence diagrams are a type of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram that illustrate the dynamic interactions between different entities or components within a system. In the context of blockchain, these diagrams can provide a comprehensive visual representation of the sequential steps involved in various blockchain processes.
By employing sequence diagrams, developers and researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the complex interactions that occur within a blockchain network. This knowledge can then be leveraged to design more efficient and secure blockchain systems, optimize existing ones, and identify potential areas for improvement.
Visualizing Blockchain Processes
To illustrate the power of sequence diagrams in the realm of blockchain, let's consider an example that showcases the interactions involved in a typical transaction validation and block creation process.
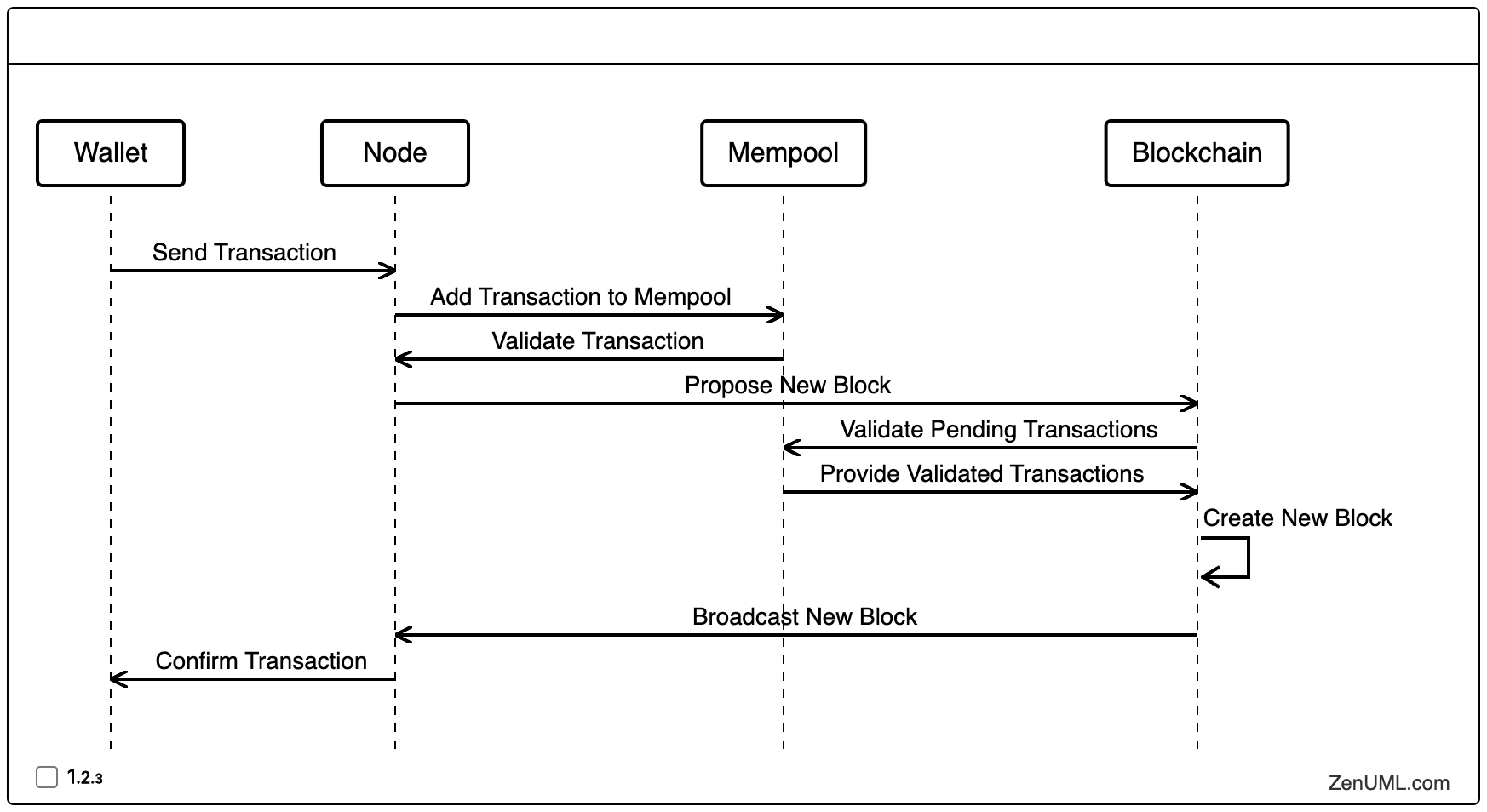
In this sequence diagram, we can observe the step-by-step interactions between the key components of a blockchain network: the Wallet, Node, Mempool, and Blockchain.
-
Transaction Initiation: The process begins with a user initiating a transaction from their Wallet, which is then sent to a Node within the network.
-
Transaction Propagation: The Node adds the transaction to the Mempool, which serves as a holding area for unconfirmed transactions.
-
Transaction Validation: The Mempool validates the transaction, ensuring its integrity and compliance with the blockchain's rules.
-
Block Proposal: The Node then proposes a new block to the Blockchain, which contains the validated transactions from the Mempool.
-
Block Creation: The Blockchain validates the pending transactions, retrieves the validated transactions from the Mempool, and proceeds to create a new block.
-
Block Broadcast: The newly created block is then broadcast to the entire network, including the Node.
-
Transaction Confirmation: Finally, the Node confirms the successful addition of the transaction to the Blockchain, informing the Wallet.
This sequence diagram provides a clear and concise visualization of the various steps involved in the transaction validation and block creation process within a blockchain network. By understanding these interactions, developers can identify potential bottlenecks, optimize the flow of information, and implement more robust security measures.
Consensus Mechanisms Unveiled
Sequence diagrams can also be leveraged to illustrate the intricate workings of different consensus mechanisms employed by blockchain networks. Consensus mechanisms are the algorithms that ensure the integrity and agreement of the distributed ledger across all nodes in the network.
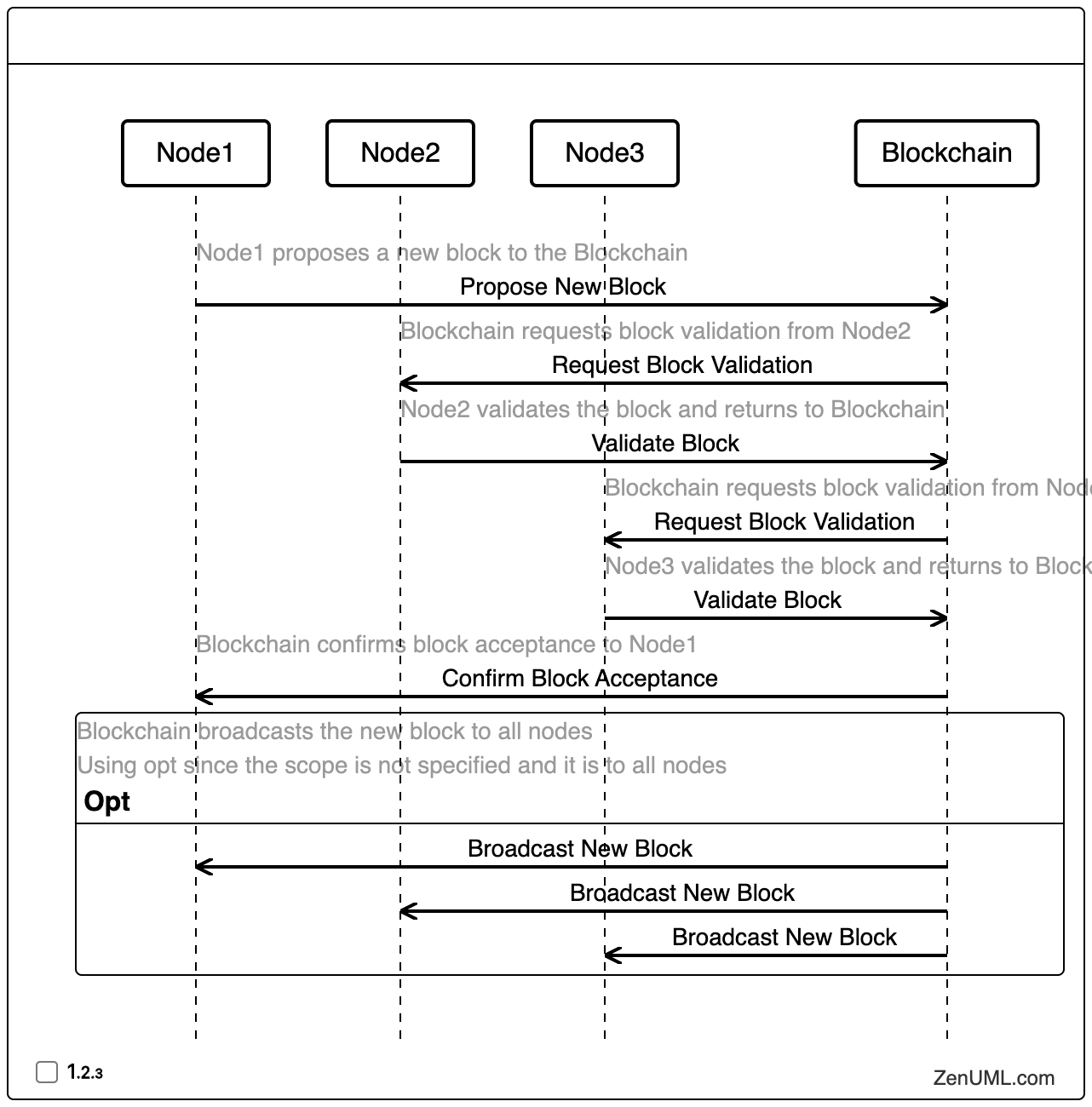
In this example, the sequence diagram depicts the consensus mechanism of a blockchain network using a majority-based validation approach. The key steps are as follows:
-
Block Proposal: Node1 proposes a new block to the Blockchain.
-
Block Validation: The Blockchain requests validation of the proposed block from other nodes in the network, in this case, Node2 and Node3.
-
Validation Response: Node2 and Node3 validate the proposed block and send their responses back to the Blockchain.
-
Block Acceptance: Once a majority of nodes have validated the block, the Blockchain confirms the block's acceptance to Node1.
-
Block Broadcast: The Blockchain then broadcasts the new block to all nodes in the network.
This sequence diagram illustrates the dynamic interactions involved in a majority-based consensus mechanism, where the Blockchain coordinates the validation process and ensures that the network reaches a consensus before finalizing the new block. By visualizing the consensus process, developers can better understand the flow of information, identify potential vulnerabilities, and design more robust consensus algorithms.
Facilitating Blockchain Design and Analysis
Sequence diagrams can play a pivotal role in the design and analysis of blockchain systems. By providing a clear and concise representation of the interactions within a blockchain network, these diagrams can aid in the following ways:
-
System Design: Sequence diagrams can help developers and architects to plan and design blockchain-based systems more effectively. They can identify the key components, their roles, and the flow of information between them, enabling the creation of more efficient and scalable blockchain architectures.
-
Process Optimization: By analyzing the sequence diagrams, stakeholders can identify potential bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for optimization within the blockchain processes. This can lead to the development of more streamlined and high-performing blockchain networks.
-
Security Evaluation: Sequence diagrams can also facilitate the assessment of the security measures within a blockchain system. By visualizing the interactions, researchers and security experts can pinpoint potential attack vectors, vulnerabilities, and areas that require enhanced security protocols.
-
Collaboration and Communication: The visual representation provided by sequence diagrams can greatly improve the collaboration and communication between different stakeholders, such as developers, business analysts, and subject matter experts. This shared understanding can foster better decision-making and alignment throughout the blockchain development lifecycle.
The Future of Blockchain Visualization
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, the need for comprehensive visualization tools will only grow. Sequence diagrams are just one example of how visual representations can unlock the complexity of blockchain networks and facilitate a deeper understanding of their inner workings.
Moving forward, we can expect to see the development of more advanced visualization techniques, including real-time monitoring dashboards, interactive simulations, and even augmented reality or virtual reality applications. These tools will empower stakeholders to gain unprecedented insights into the dynamic behavior of blockchain networks, enabling them to design, optimize, and secure these systems with greater precision and confidence.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Blockchain Enigma
In the rapidly transforming world of blockchain technology, sequence diagrams have emerged as a powerful tool for unveiling the complex interactions that underpin these decentralized networks. By providing a clear visual representation of the sequential steps involved in various blockchain processes, these diagrams can aid developers, researchers, and enthusiasts in comprehending the inner workings of these systems.
As we have explored in this article, sequence diagrams can elucidate the dynamics of transaction validation, block creation, and consensus mechanisms, ultimately facilitating the design, optimization, and security evaluation of blockchain-based applications. With the continued evolution of blockchain visualization techniques, the future holds even greater promise for unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology.
We invite you, our readers, to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Your insights and perspectives can further enrich our understanding of the role of sequence diagrams in the ever-expanding blockchain ecosystem.
Try ZenUML now!
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.